Solving the Problems of Cellular Capacity Constraints, Outages and Technology Upgrades with Portable Telescoping Masts

Issues facing today’s cellular network infrastructure
Several issues can stress the capacity and capabilities of a cellular network. The data requirements driven by the advent of the “smart phone” have introduced data demands on already strained networks that cannot afford additional pressure from natural and man-made disasters, temporary and localized increases in data demand and temporary capacity reduction due to technology upgrades or equipment maintenance. The problems created by these issues are well-documented but they can be conquered with the proper equipment, technology and deployment strategy.
Three major challenges

Collapsed cell tower replaced with portable cellular site with telescoping mast
In order to properly safeguard a network from these challenges, one must fully understand their impact. Natural disasters can disable cellular towers via high winds, fires, flooding or earthquakes. For instance, Hurricane Sandy that hit the highly populated east coast of the United States; disabled 25% of the cellular network. Man-made accidents or sabotage disrupt networks as well. Cellular demand increases dramatically during and after the event as the population attempts to connect with emergency services, family and friends. Disaster recovery agencies and the first responders that operate them will also add traffic to the crippled network once they arrive. Depending on the disaster, the area affected can be localized or stretch for kilometers, requiring multiple deployment strategies employing varying amounts of equipment.
Public events, where thousands of people gather for hours or even days, can overwhelm the fixed cellular network infrastructure designed for the permanent population of the area. Sporting events and other social gatherings bring together thousands of people eager to share their experience via their connected “smart devices”. The data load from this influx of people requires additional but temporary data transfer capacity.

Adding cellular capacity with a light truck equipped with a telescoping mast
Technology upgrades and periodic maintenance requires strategies and tactics that enable users to remain connected during a period that can sometimes stretch to several months. The transition from analog to 2G, 3G and 4G technologies require that users remain connected during a pre-determined transition period which will often require a doubling of cellular antennas needed for a location. Equipment must be available to support both the older technology and the newly deployed technology. Periodic maintenance which requires a cellular site to be taken off-line for repair or refurbishment requires a temporary solution that does not inconvenience cellular data users.
4G LTE introduction
Cellular carriers in the United States continue the rollout of 4G technology that began in earnest in 2011. 700 MHz /LTE (Long Term Evolution) technology is the most widely used. The technology upgrade has provided speed that can exceed standard Wi-Fi. Below is a table that compares the technologies.
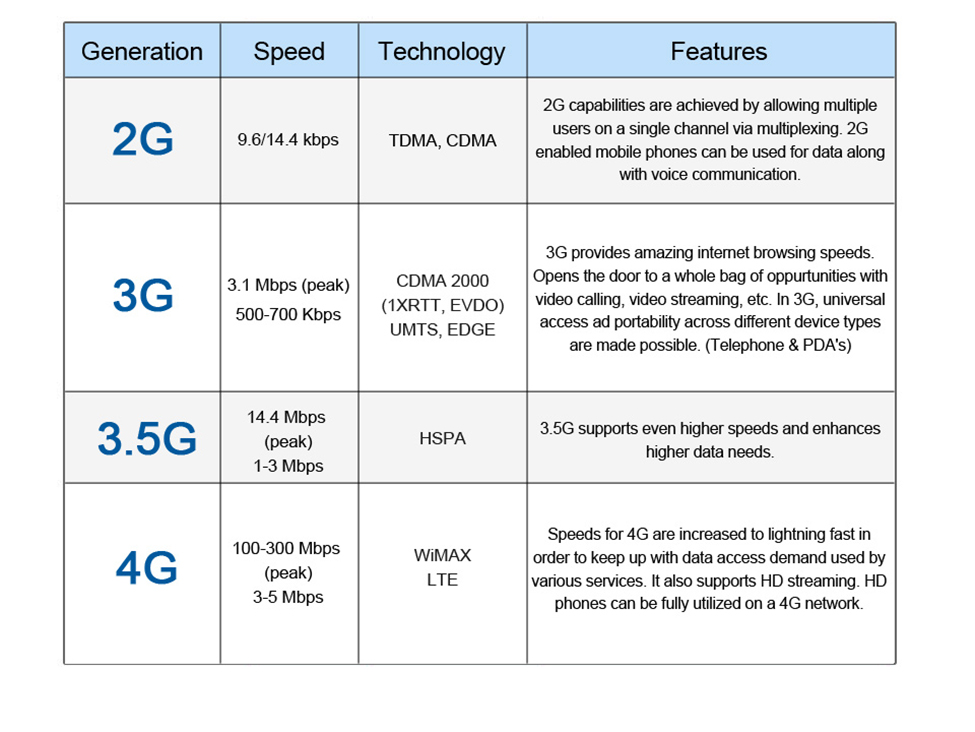
Figure 1: Cellular Technology Comparison
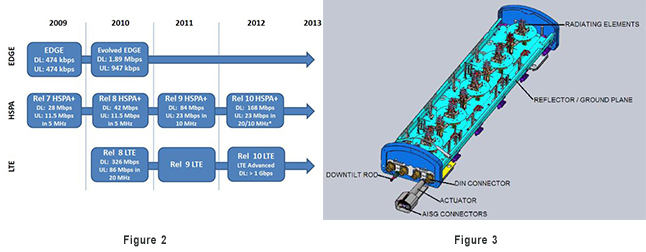
Figure 2: USA 3GPP Technology Evolution1
(Source: Transition to 4G: 3GPP Broadband Evolution
to IMT-Advanced,Rysavy Research 2010 White Paper)
Figure 3: Diagram of typical LTE Antenna
LTE antennas vary in size and weight. The average weight of a one sector antenna ranges from 16 – 27 kg and measures 9 cm deep by 30 cm wide by 182 cm in height. The surface area of the antenna can produce significant wind load that must be considered in any application. Another important consideration is the weight of the cables and the wind load they add. 2 x 6 cable arrangements are typically used to reduce the wind load.
Portable cellular sites deliver the solution
Portable temporary cellular sites can aid a communications provider in overcoming the aforementioned challenges. These portable sites include the equipment, shelter and elevation solutions needed to supplement existing or replace lost data transmission capacity. Typically portable cellular sites are trailer or light-truck based and are designed for deployment periods of a few days to several months of autonomous operation when equipped with electric generators. One of the most critical components of any portable cellular platform is the antenna elevation provided by a telescopic mast.

Dual telescoping masts on a portable cellular site trailer
Telescoping masts serve as the all-important elevation solution for cellular antennas deployed via a temporary platform. The optimal height of 18 meters provides clearance for most obstructions and is the most common height in use. Lower heights are typically sufficient when temporary capacity constraints arise due to an influx of users in a localized area. In some cases, temporary cellular platforms with masts achieving heights of 30 meters are deployed when a large, permanent cellular transmission site is off-line due to maintenance or disaster.
A mast must not only reach the necessary height to meet the defined objective but it must also safely elevate the antenna and significant cable payload while minimizing twist and deflection. Substantial movement can degrade the signal, minimizing the benefit of the deployment.
Will-Burt pneumatic masts provide proven and reliable elevation
The Will-Burt Company offers an extensive line of field-proven telescopic masts designed and manufactured in the USA to meet the demanding requirements of the worldwide mobile cellular site market. Will-Burt’s telescoping pneumatic masts deliver a lightweight yet strong elevation solution that minimizes twist with dual keyways and reduces deflection with strong anodized aluminum, in turn, delivering one of the most accurate and precise pointing masts available.

Light trucks with telescoping masts deployed after Hurricane Katrina
The lightweight design of the Will-Burt mast does not require a heavy trailer or truck; this allows valuable payload capacity for other equipment which is not available when hydraulic and / or steel masts are installed. No environmentally hazardous hydraulic fluid is required for elevation; Will-Burt pneumatic masts require only air. Also, multiple Will-Burt masts can be installed on the same platform which increases cellular data throughput without overloading the truck or trailer. This ultimately lowers the overall cost of equipment and deployment.
Will-Burt’s locking pneumatic masts can be deployed for extended periods of time because they do not require constant air pressure. Air is only required for raising and lowering the mast, the mast can remain deployed for an indefinite period of time when the locks are engaged.
Finally, Will-Burt’s masts are available in a variety of heights and payload capacities. Heights can reach 30 meters or more and payload capacities are available up to 540kg.

Three 4G LTE sector antennas deployed on a Will-Burt pneumatic telescoping mast on a light truck
Typical mobile cellular platforms will make use of a mast that is 18 meters in height with a payload capacity of 200 kg. This is more than sufficient to manage 3 4G LTE antennas and the corresponding cable payload. Three antennas arranged at 120° intervals will provide optimal 360° sector coverage. Omni-directional antennas are also used; typically positioned opposite of each other.
A telescoping pneumatic mast with a payload capacity of 540 kg allows for placement of up to 3 antenna arrays containing up to a total of 9 LTE antennas. This allows for greater data throughput with a smaller space claim.
The Will-Burt Company manufactures its telescopic pneumatic masts in the USA using an ISO 9001:2008 certified quality system, which delivers quality products time after time. Special design and program requirements that are not met with a catalog mast can be developed by Will-Burt’s team of experienced and specially trained engineers.
The Will-Burt Company delivers premier elevation solutions for portable cellular sites that address the critical issues of capacity constraints, outages and technology upgrades.






